Introduction -
Born in Reading, Pennsylvania [1909] -
Graduated from a diploma program in Pottstown, Pennsylvania in 1931. -
Done BA in interpersonal psychology from Bennington College in 1943. -
MA in psychiatric nursing from Colombia University New York in 1947. -
EdD in curriculum development in 1953. -
Professor emeritus from Rutgers university -
Started first post baccalaureate program in nursing -
Published Interpersonal Relations in Nursing in 1952 -
1968 :interpersonal techniques-the crux of psychiatric nursing -
Worked as executive director and president of ANA. -
Worked with W.H.O, NIMH and nurse corps. -
Died in 1999.
Psychodynamic nursing -
Understanding of ones own behavior -
To help others identify felt difficulties -
To apply principles of human relations to the problems that arise at all levels of experience -
In her book she discussed the phases of interpersonal process, roles in nursing situations and methods for studying nursing as an interpersonal process. -
According to Peplau, nursing is therapeutic in that it is a healing art, assisting an individual who is sick or in need of health care. -
Nursing is an interpersonal process because it involves interaction between two or more individuals with a common goal. -
The attainment of goal is achieved through the use of a series of steps following a series of pattern. -
The nurse and patient work together so both become mature and knowledgeable in the process.
Definitions -
Person :A developing organism that tries to reduce anxiety caused by needs -
Environment : Existing forces outside the organism and in the context of culture -
Health : A word symbol that implies forward movement of personalitycreative, constructive, productive, personal and community living. and other ongoing human processes in the direction of -
Nursing: A significant therapeutic interpersonal process. It functions cooperatively with other human process that make health possible for individuals in communities
Roles of nurse -
Stranger: receives the client in the same way one meets a stranger in other life situations provides an accepting climate that builds trust. -
Teacher: who imparts knowledge in reference to a need or interest -
Resource Person : one who provides a specific needed information that aids in the understanding of a problem or new situation -
Counselors : helps to understand and integrate the meaning of current life circumstances ,provides guidance and encouragement to make changes -
Surrogate: helps to clarify domains of dependence interdependence and independence and acts on clients behalf as an advocate. -
Leader : helps client assume maximum responsibility for meeting treatment goals in a mutually satisfying way
Additional Roles include: 1. Technical expert
2. Consultant
3. Health teacher
4. Tutor
5. Socializing agent
6. Safety agent
7. Manager of environment
8. Mediator
9. Administrator
10. Recorder observer
11. Researcher Theory of interpersonal relations Identified four sequential phases in the interpersonal relationship: 1. Orientation
2. Identification
3. Exploitation
4. Resolution Orientation phase -
Problem defining phase -
Starts when client meets nurse as stranger -
Defining problem and deciding type of service needed -
Client seeks assistance ,conveys needs ,asks questions, shares preconceptions and expectations of past experiences -
Nurse responds, explains roles to client, helps to identify problems and to use available resources and services
Factors influencing orientation phase 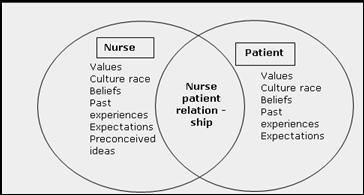
Identification phase
Exploitation phase -
Use of professional assistance for problem solving alternatives -
Advantages of services are used is based on the needs and interests of the patients -
Individual feels as an integral part of the helping environment -
They may make minor requests or attention getting techniques -
The principles of interview techniques must be used in order to explore, understand and adequately deal with the underlying problem -
Patient may fluctuates on independence -
Nurse must be aware about the various phases of communication -
Nurse aids the patient in exploiting all avenues of help and progress is made towards the final step
Resolution phase -
Termination of professional relationship -
The patients needs have already been met by the collaborative effect of patient and nurse -
Now they need to terminate their therapeutic relationship and dissolve the links between them. -
Sometimes may be difficult for both as psychological dependence persists -
Patient drifts away and breaks bond with nurse and healthier emotional balance is demonstrated and both becomes mature individuals
Interpersonal theory and nursing process -
Both are sequential and focus on therapeutic relationship -
Both use problem solving techniques for the nurse and patient to collaborate on, with the end purpose of meeting the patients needs -
Both use observation communication and recording as basic tools utilized by nursing
Assessment - Data collection and analysis [continuous]
- May not be a felt need
| Orientation - Non continuous data collection
- Felt need
- Define needs
| Nursing diagnosis
Planning | Identification - Interdependent goal setting
| Implementation - Plans initiated towards achievement of mutually set goals
- May be accomplished by patient , nurse or family
| Exploitation - Patient actively seeking and drawing help
- Patient initiated
| Evaluation - Based on mutually expected behaviors
- May led to termination and initiation of new plans
| Resolution - Occurs after other phases are completed successfully
- Leads to termination a
| Peplau’s work and characteristics of a theory -
Theories can interrelate concepts in such a way as to create a different way of looking at a particular phenomenon. Four phases interrelate the different components of each phase.
-
The nurse patient interaction can apply to the concepts of human being, health, environment and nursing.
-
Theories must be logical in nature. This theory provides a logical systematic way of viewing nursing situations
-
Key concepts such as anxiety, tension, goals, and frustration are indicated with explicit relationships among them and progressive phases
-
Theories should be relatively simple yet generalizable. It provides simplicity in regard to the natural progression of the NP relationship. Leads to adaptability in any nurse patient relationship.
-
The basic nature of nursing still considered an interpersonal process
-
Theories can be the bases for hypothesis that can be tested.Has generated testable hypotheses.
-
Theories contribute to and assist in increasing the general body of knowledge within the discipline through the research implemented to validate them. In 1950’s two third of the nursing research concentrated on N-P relation ship.
-
Theories can be utilized by practitioners to guide and improve their practice. Peplau’s anxiety continuum is still used in anxiety patients
-
Theories must be consistent with other validated theories, laws, and principles but will leave open unanswered questions that need to be investigated. Consistent with various theories
Limitations -
Intra family dynamics, personal space considerations and community social service resources are considered less -
Health promotion and maintenance were less emphasized -
Cannot be used in a patient who doesn’t have a felt need eg. With drawn patients, unconscious patients -
some areas are not specific enough to generate hypothesis
Research Based on Peplau’s Theory -
Hays .D. (1961).Phases and steps of experimental teaching to patients of a concept of anxiety: Findings revealed that when taught by the experimental method, the patients were able to apply the concept of anxiety after the group was terminated. -
Burd .S.F. Develop and test a nursing intervention framework for working with anxious patients: Students developed competency in beginning interpersonal relationship
References -
Timber BK. Fundamental skills and concepts in Patient Care, 7th edition, LWW, N -
George B. Julia , Nursing Theories- The base for professional Nursing Practice , 3rd ed. Norwalk, Appleton & Lange. -
Wills M.Evelyn, McEwen Melanie (2002). Theoretical Basis for Nursing Philadelphia. Lippincott Williams& wilkins. -
Meleis Ibrahim Afaf (1997) , Theoretical Nursing : Development & Progress 3rd ed. Philadelphia, Lippincott. -
Taylor Carol,Lillis Carol (2001)The Art & Science Of Nursing Care 4th ed. Philadelphia, Lippincott. -
Potter A Patricia, Perry G Anne (1992) Fundamentals Of Nursing –Concepts Process & Practice 3rd ed. London Mosby Year Book. -
Vandemark L.M. Awareness of self & expanding consciousness: using Nursing theories to prepare nurse –therapists Ment Health Nurs. 2006 Jul; 27(6) : 605-15 -
Reed PG, The force of nursing theory guided- practice. Nurs Sci Q. 2006 Jul;19(3):225 -
Delaune SC,. Ladner PK, Fundamental of nursing, standard and practice, 2nd edition, Thomson, NY, 2002.
|

Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar